Description
One of the most studied probiotics in the world
BioGaia’s probiotic products with Lactobacillus reuteri are among the most scientifically well-documented probiotics in the world with regard to both efficacy and safety. To date, the efficacy and safety of BioGaia’s different strains of L. reuteri have been documented in 203 clinical studies in 17,200 people of all ages. Lactobacillus reuteri has shown results in 105 clinical studies in children, from newborns up to 18 years old, and 98 studies in adults. Probiotic strains that have been used in clinical trials are L. reuteri Protectis (DSM 17938), L. reuteri Gastrus (ATCC PTA 6475), and L. reuteri Prodentis (L. reuteri DSM 17938 and Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC PTA 5289). Results have been published in 180 papers in scientific journals (February 2019).Safe for all ages
Safety has been proven in preterm babies, infants, children, healthy adults, and immune-compromised adults. No serious adverse effects have been observed up to the maximum tested dosage of 10 billion CFU per day, meaning 1000 times the recommended daily dose. Lactobacillus reuteri is considered safe as it fulfills the following criteria:- Human origin
- Named and classified according to correct taxonomy
- Manufactured under controlled conditions to eliminate contamination
- Safety is evaluated and documented on target population
- Harbors no toxins or transferrable antibiotic resistance genes
What are probiotics?
Dosage and colonization
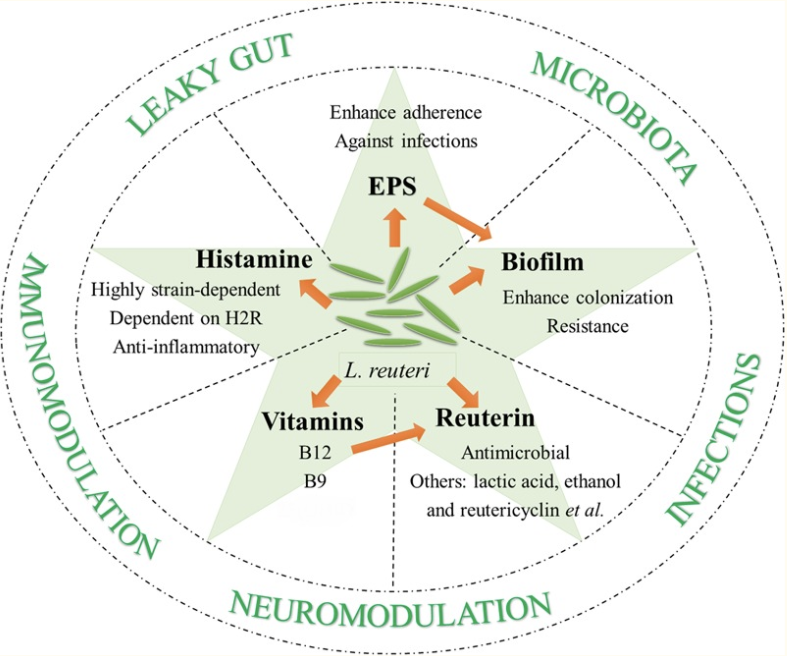
Based on clinical data, 100 million CFU per day has been chosen as a safe and efficient dose of Lactobacillus reuteri Protectis for children and adults. The recommended dosage of probiotic bacteria depends on which strain or strains the product contains. For some probiotic strains, a relatively low amount of bacteria is needed, while other strains require a larger amount. The epithelial lining covers our gastrointestinal tract and works like a skin on the inside of our bodies. The main task of our ”inner skin” is to differentiate between what should be absorbed and what should not be let into our bodies. Biopsies have shown that Lactobacillus reuteri is temporarily binding to our epithelial lining. However, since the cells in our epithelial lining is replaced every fourth day, the majority of L. reuteri cells are also washed away within a week or so. Since L. reuteri colonization is transient, everyday intake is recommended to ensure adequate and stable levels of L. reuteri in the gastrointestinal tract. Colonization of L. reuteri Protectis has been proven throughout the entire human gastrointestinal tract using the biopsies technique.The origin of Lactobacillus reuteri
The first strain of Lactobacillus reuteri (L. reuteri) for human use, L. reuteri DSM 17938, was isolated in 1990 from the breast milk of a Peruvian mother living in the Andes. The commercial name is L. reuteri Protectis. Other human strains from BioGaia are L. reuteri ATCC PTA 5289 and ATCC PTA 6475. L. reuteri ATCC PTA 5289 used in oral health products was isolated from the oral cavity of a Japanese woman with remarkably good dental status and L. reuteri ATCC PTA 6475 was isolated from the breast milk of a Finnish woman.
Bacteria of human origin
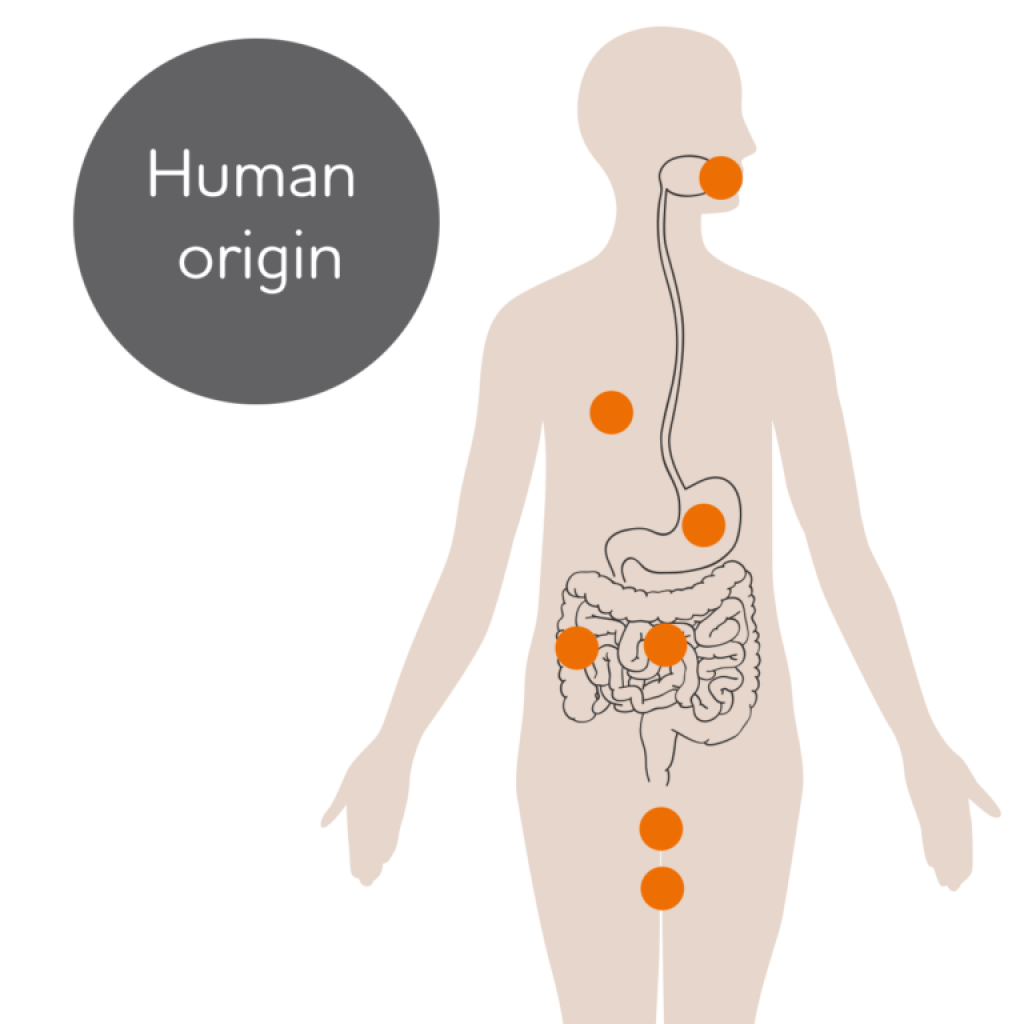
All our commercial strains are of human origin, naturally, colonize humans, and are therefore more likely to actually have a positive effect on human health. Even an indigenous bacterium like BioGaia’s L. reuteri Protectis should be taken on a regular basis, to reach high enough levels to achieve proper colonization and have a good effect. L. reuteri has been found in:- Breast milk
- The vagina
- The mouth
- The stomach
- The small intestine
- The large intestine
- Feces












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.