- 8 months ago
- 12Minutes
- 2618Words
- 714Views
Wild Yam is a little different from your conventional eating yam. The Wild Yam has powerful medicinal properties and was used to make the first birth control pills. Today it is used widely in the natural products industry to help balance sex hormones.
In this article, we will discuss what the active compounds are, how it works, and the supporting scientific evidence.
(1) University of Maryland Medical Center. Wild Yam. http://www.umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/herb/wild-yam
(2) The clinical use of dehydroepiandrosterone in postmenopausal women. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23965649
(3) DHEA therapy for women: effect on sexual function and wellbeing.
(4) The safety of 52 weeks of oral DHEA therapy for postmenopausal women. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19410392
(5) Dehydroepiandrosterone improves psychological well-being in male and female hypopituitary patients on maintenance growth hormone replacement. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16849414
(6) Dehydroepiandrosterone therapy as female androgen replacement. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16633983
(7) Dehydroepiandrosterone administration in humans: evidence based? PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16186639
(8) Androgen therapy with dehydroepiandrosterone. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14551720
(9) [DHEA: orthodox or alternative medicine?]. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11680205
(10) A comparison of dehydroepiandrosterone and 7-keto dehydroepiandrosterone with other drugs that modulate ethanol intake in rats responding under a multiple schedule. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3360959/#R1
(11) Difference Between 7-Keto DHEA and DHEA. http://www.differencebetween.net/science/biology-science/differences-between-7-keto-dhea-and-dhea/
(12) Final report of the amended safety assessment of Dioscorea Villosa (Wild Yam) root extract. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15513824
(13) 7-oxo-DHEA and Raynaud’s phenomenon. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12581618
(14) Bioassay-guided evaluation of Dioscorea villosa – an acute and subchronic toxicity, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory approach. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3734200/
(15) Lipidated Steroid Saponins from Dioscorea villosa (Wild Yam). PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3935402/
(16) Diosgenin: Recent Highlights on Pharmacology and Analytical Methodology. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5225340/
(17) Neurobiological and Neuropsychiatric Effects of Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEA Sulfate (DHEAS). PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2725024/
(18) HUM5007, a novel combination of thermogenic compounds, and 3-acetyl-7-oxo-dehydroepiandrosterone: each increases the resting metabolic rate of overweight adults. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17418559/
(19) Ergosteroids: induction of thermogenic enzymes in liver of rats treated with steroids derived from dehydroepiandrosterone. PUBMED https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC41569/
(20) UMIB SUMMIT PROCEEDINGS. PUBMED. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4993095/
(21) Wild Yam, WebMD http://www.webmd.com/vitamins-supplements/ingredientmono-970-wild%20yam.aspx?activeingredientid=970&activeingredientname=wild%20yam
Wild Yam Description
Also known as colic root, wild yam is a twining, tuberous vine. One species is native to North America; another is native to China. Both contain diosgenin and have similar medicinal properties. There are an estimated 600 species of yam in the genus Dioscorea. Many of them are wild species that flourish in damp woodlands and thickets, and not all of them contain the medicinally active part, diosgenin. (1)
Some species are grown specifically as a source of diosgenin for laboratories to use in making steroids. These species are generally not eaten due to a bitter flavor. Only about 12 of the 600 species are considered edible. (21)

Wild Yam History
In the 18th and 19th centuries, herbalists used wild yam (Dioscorea villosa) to treat menstrual cramps and problems related to childbirth, as well as for upset stomach and coughs. In the 1950s, scientists discovered that the roots of wild yam (not to be confused with the sweet potato yam) contain diosgenin. Diosgenin is a phytoestrogen or plant-based estrogen, that can be chemically converted into a hormone called progesterone. Diosgenin was used to make the first birth control pills in the 1960s. (1)
Wild Yam Traditional Uses
Dioscorea villosa (DV) has been used in Brazil as an alternative medicine to attenuate menopause symptoms, as well as for the treatment of joint pain and rheumatoid arthritis. (14)
Some women apply wild yam creams to the skin to reduce menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes. (21)
Wild Yam Active Constituents
Dioscorea Villosa (Wild Yam) Root Extract is an extract of the rhizomes of the wild yam. The extract contains glycoside and steroidal saponins (< or =0.4%), diosgenin (< or =3.5%), alkaloids, tannins, phytosterols, and starch. (12) The chemical composition of Wild Yam also includes protodioscin, methylprotodioscin, dioscine, prosapogenin, epiafzelechin glucopyranoside, saponin glycosides, and phytoestrogen. (14)
Although only one use was reported to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (in a body and hand preparation), the industry reported uses in body and hand creams, lotions, powders, and sprays at a concentration of 0.00001%, and in moisturizing creams, lotions, powders, and sprays at concentrations up to 15%. (12)
Two groups of lipidated steroid saponins including seven new compounds were isolated from the widely used botanical, wild yam (Dioscorea villosa), employing a fractionation protocol of metabolomic mining. This methodology has very recently led to the isolation of 14 diarylheptanoids from the same plant. (15)
Diosgenin
The rhizomes and roots of Dioscorea villosa is an important source of diosgenin, a phytoestrogen that has been investigated thoroughly from both chemical and biological perspectives. (15)
This steroid is of high industrial importance and has been the subject of interest to many researchers worldwide over the years. In fact, most of the therapeutically useful steroidal drugs, including sex hormones and corticosteroids, are produced in a semi-synthetic fashion from natural precursors and predominantly from diosgenin. (15)
Diosgenin itself has several important biological activities also with a great interest for the pharmaceutical industry. In fact, diosgenin has been described in the literature for its pharmacological potential, including the interesting underlying mechanisms of action, thereby confirming and extending the knowledge from its usage in traditional medicine. (15)
In this context, mainly over the past two decades, a series of preclinical and mechanistic studies have been performed to understand the real importance and benefits of diosgenin against a variety of pathologies including metabolic diseases (diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia, including hypercholesterolemia), inflammatory diseases, and cancer. (15)
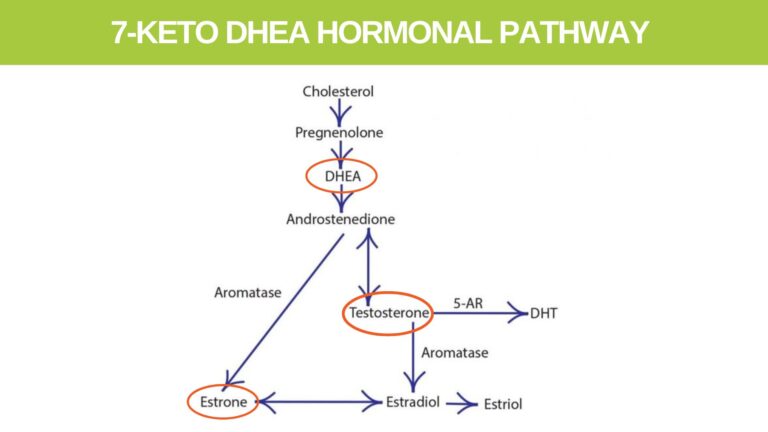
DHEA in Wild Yam
Plain DHEA is not found in the Wild Yam plant, but the breakdown product 7-keto DHEA is produced from Wild Yam extract, diosgenin. Due to the similar nature of DHEA, Diosgenin and Wild Yam extract and their actions, I thought we should take a moment to investigate and understand this area better.
The exact physiological role of DHEA remains unknown, but DHEA supplementation has recently been proven beneficial in typical deficient states like adrenal insufficiency or major depressive illnesses. (9)
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its sulphate DHEAS are the most abundant circulating sex steroid hormones in women, providing a large precursor reservoir for the intracellular production of androgens and oestrogens in non-reproductive tissues. Levels of DHEA and DHEAS decline with age. It has been proposed that restoring the circulating levels of these steroids to those found in young people may have anti-aging effects and improve well-being and sexual function. (3)
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is an abundant circulating androgen precursor preferentially produced by the adrenal glands. DHEA has been shown to exert its effects via downstream conversion to sex steroid hormones, neuromodulation, improvement in endothelial cell function, and possibly by acting on a cell membrane-bound receptor. Low levels of circulating DHEA have been demonstrated in women with diminished libido and other symptoms of sexual dysfunction. (6)
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its ester dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) are produced by the adrenal glands. These hormones are inactive precursors that are transformed into active sex steroids in peripheral target tissues. After a peak in early adulthood, there is a marked decrease in plasma concentrations throughout adult life. These hormones are thought to affect mood and well-being, have neurosteroid effects, and may influence the immune system. (7)
With the evidence currently available, however, one can reasonably suggest that dehydroepiandrosterone offers the promise of safe and efficient replacement therapy for specific symptoms common to postmenopausal women. (2)
DHEA replacement leads to modest improvement in psychological well-being in females and minor psychological improvement in males with reduced pituitary gland functions. (5)
Some studies suggest a favorable effect of pharmacological doses of DHEA in the treatment of depression. DHEA may have a very limited effect on cognitive function in elderly people, and some studies suggest a beneficial immunomodulatory effect of DHEA in patients with autoimmune diseases (7)
Beneficial effects seem plausible in women with several conditions according to the results of double-blind placebo-controlled trials: the dose of 30 to 50 mg seems beneficial to the mood, sense of well-being, and sexual desire and activity of women with adrenal insufficiency. The only long-term trial of supplementation devoted to women over 60 reported significant increases in bone mineral density and, in the 70-79-year-old subgroup, in sexual desire, arousal, activity, and satisfaction. (8)
The dose of 200 mg also proved to decrease disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lastly, high DHEA doses have improved mood in various groups of patients of any age and gender with depressive symptoms. The use of DHEA therapy may also be discussed in women of any age when a trial of androgen supplementation seems justified because of the existence of an inhibited sexual desire or a sexual arousal disorder associated with documented androgen deficiency. (8)
So what about 7-Keto DHEA, what’s the difference?
7-keto DEHA and DHEA – The difference between them
7_Keto DHEA can be synthesized from the diosgenin extract of Wild Yam. 7-Keto DHEA is a metabolite of DHEA. It is a metabolite of a hormone that can enhance immune functioning and help in reducing body fat. 7-Keto DHEA is formed when DHEA breaks down. It is twice as effective as DHEA. (11)
The major difference between DHEA and 7-Keto DHEA is that DHEA converts to testosterone and estrogen while 7-Keto DHEA does not convert into these two sex-related hormones. (11)
7-keto DHEA would also have a distinct advantage over DHEA as a treatment for alcohol abuse and dependence in that it does not act as a precursor for the sex hormones. (10)
7-keto DHEA has been shown to be well tolerated in humans at doses as high as 200 mg/kg and is available over the counter as well as in some nutritional supplements. These characteristics of 7-keto DHEA suggest that it may have therapeutic advantages over DHEA (10)
Wild Yam Scientific Evidence
Wild Yam
Because the treatment of menopause with synthetic hormones might lead to increases in cholesterol, our findings suggest that Wild Yam dry extract could be regarded as a safer phytomedicine to control climacteric symptoms without causing side effects on serum fat levels. (14)
Because there are so many constituents in Wild Yam we will discuss only the two major therapeutic components here.
Diosgenin
Diosgenin, a steroid saponin that is found in a number of plant species, is reported to be a promising bioactive biomolecule with diverse important medicinal properties, including hypolipidemic, hypoglycemic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiproliferative activities. (16)
Anti-cancer
Several preclinical studies investigated the effects of the diosgenin as a chemopreventive/therapeutic agent against cancers of several organs, and this has demonstrated the high interest of this molecule as a potential antitumor agent. (16)
Diosgenin also has antimetastatic effects; for example, it was demonstrated that it can inhibit the migration of human breast cancer. (16)
Immune function
The anti-inflammatory activity of diosgenin is a known relevant effect of this steroid and has a relevant interest in a variety of pathologies. (16)
Anti-inflammatory
As osteoarthritis is characterized by progressive destruction of articular cartilage and synovial inflammation, diosgenin can also be of interest in this disease due to its anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties. (16)
Obesity
Diosgenin can be useful in the treatment of diabetes by promoting adipocyte differentiation and by inhibiting inflammation in adipose tissues. Therefore, diosgenin may be useful to improve the patient’s condition in the glucose metabolic disorder associated with obesity. In this context, in other experimental models, it was observed that diosgenin led to a reduction of plasma and hepatic triglycerides in obese diabetic mice and may be useful for the management of diabetes-related hepatic dyslipidemias. (16)
Circulation
In in vitro and in vivo models it was demonstrated that diosgenin exerts antithrombotic activity via inhibition of platelet aggregation and thrombosis. In addition, more recently it was again demonstrated that this steroid and a structural analog act by inhibiting platelet aggregation, which prevents blood coagulation. (16)
7-Keto DHEA (also known as 7-oxo-DHEA)
Post Traumatic Stress
Recently, five cases of “remarkable benefits” have been reported after extremely treatment-resistant patients with PTSD were administered 7-keto DHEA (25–150 mg per day) in an open-label manner. All five of these patients had baseline serum DHEAS concentrations in the lowest quartile of the normal range.
The responses in the patients were rapid, occurring within days, and were both subjectively and objectively discernible. 7-keto DHEA was chosen instead of the parent compound DHEA because the 7-keto moiety is not aromatized to testosterone or estrogen and because it may have superior anti-glucocorticoid properties. (17)
Addiction
7-Keto DHEA has been shown to decrease the drive to consume alcohol. Common adverse effects in women taking 200 mg of DHEA per day include acne and hirsutism. These effects may be averted, however, by administering 7-keto DHEA, which is not converted to sex hormones and reduces alcohol intake similarly to DHEA.
Metabolic Rate (Thermogenisis)
In One study 30 women, 10 men; mean age, 38.5 years found that 7-Keto increased resting metabolic rate above basal levels and may benefit obese individuals with impaired energy expenditure. (18)
These 7-oxygenated DHEA derivatives are active inducers of these thermogenic enzymes in rats and the 7-oxo derivatives are more active than the parent steroids. We postulate that the 7 alpha-hydroxy and 7-oxo derivatives are on a metabolic pathway from DHEA to more active steroid hormones. These 7-oxo steroids have potential as therapeutic agents because of their increased activity and because they are not convertible to either testosterone or estrogens. (19)
7-Keto DHEA is relatively non-toxic to the body. It may eliminate or significantly reduce the possible side effects of plain DHEA. It is also more thermogenic and supports peripheral blood circulation. As an ergogenic (thermogenic) steroid, 7-oxo-DHEA, which is available without prescription as the trademarked 7-keto DHEA, may be very helpful in the prevention of primary Raynaud’s attacks by increasing the basal metabolic rate and inhibiting vasospasm. (13)
The obtained data from another study demonstrated that 7-oxo-DHEA is a more potent metabolic modulator than plain DHEA. (20)
Adverse effects
It was concluded that Dioscorea Villosa (Wild Yam) Root Extract is safe as used in cosmetic formulations. This conclusion regarding safety, however, is valid only for extracts prepared in a manner that produces a similar chemical profile as that described in this report, particularly as regards diosgenin. (12)
No adverse effects were reported in postmenopausal women using DHEA for 52 weeks at the dosage of 50mg daily. (4)
Findings indicate that oral Wild Yam promotes no morphological changes in the vital organs of animals and suggest that this substance produces no toxicological effects. (14)
Conclusion
There is a long history of Wild Yam being used to support hormonal health and an emerging body of evidence to support this tradition.
Wild Yam extracts contain hormonally active compounds such as Diosgenin and 7-Keto DHEA which have proven to support the immune system, balance addictive behaviour, reduce stress and support metabolism and circulation. All of these functions lean towards helping control a negative eating pattern and losing weight by way of supporting the body in a holistic fashion.
Wild Yam Extract in the form of 7-keto DHEA (50gm per capsule/sachet) can be found in the following products:
- Cleansa 120 capsules
- The Ultimate Herbal SLIM 480 capsules
- BodiTune 32 Sachets



